MODEL
Modelling the Energy Development under Environmental and Socioeconomic constraints – MEDEAS
- Geographical scope:Global, Regional
- Model type:Integrated assessment model
- Time horizon:1995-2050
- Initial Release:2018
- Institution(s):ICM-CSIC - (Coordinator) Institut of Marine Sciences - Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, AEA - Austrian Energy Agency, ARU - Anglia Ruskin University, B4Y - Blue4You - Fine Art in Web Technologies, BSERC - Black Sea Energy Research Centre, CRES - Centre for Renewable Energy Sources and Saving, DUHA - Hnuti DUHA, IIASA - International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis, INSTM - National Interuniversity Consortium of Materials Science and Technology, MU - Masaryk University, UVA - Universidad de Valladolid
- Link:https://www.medeas.eu/model/medeas-model
- Contact:Institute of Marine Sciences (CSIC)
- Contact e-mail:info@medeas.eu
MEDEAS-World model is a global, one region-aggregated economy-energy-environment model which runs from 1995 to 2050.
MEDEAS-World model serves as framework for the development and evolution of the European model version, which is the core of the MEDEAS project.
MEDEAS-World model has been designed applying System Dynamics, which facilitates the integration of knowledge from different perspectives as well as the feedbacks from different subsystems.
The model, originally built in Vensim DSS software for Windows Version 6.4E (x32), is being translated to Python programming language (open source) – available from January 2018
MEDEAS-World model consists of a modular and flexible structure, where each module can be expanded/simplified/replaced by another version or submodel. The model is structured into 7 submodules:
- Economy: The economy of MEDEAS is modelled following a post-Keynesian approach assuming disequilibrium (i.e. non-clearing markets), demand-led growth and supply constraints. The economic structure is captured by the integration of IOA (35 industrial sectors and households).
- Energy: This module includes the renewable and non-renewable energy resources potentials and availability taking into account biophysical and temporal constraints. In total, 5 final fuels are considered (electricity, heat, solids, gases and liquids) and a diversity of energy technologies are modelled. A net energy approach has been followed.
- Infrastructures: Energy infrastructures represent the infrastructures of power plants to generate electricity and heat.
- Materials: Materials are required by the economy and MEDEAS especially tracks the material requirements for the construction and O&M of the energy infrastructures. The extraction demands are subsequently compared with the levels of available metrics of reserves and resources.
- Land Use: this is the less developed module of MEDEAS, and it mainly accounts for the land requirements of the RES energies.
- Climate Change: This module projects the climate change levels due to the GHG emissions generated by the human societies, which also feed-back through a damage function.
- and Social and Environmental Impacts Indicators: this module translates the “biophysical” results of the simulations into metrics related with social and environmental impacts. The objective of this module is to contextualize the implications for human societies in terms of well-being for each simulation.
The modules of economy and energy are the most extensive and reach the highest degree of disaggregation. Interrelations between the 7 modules: the main variables that connect the different modules are represented by arrows. Most modules have bi-directional linkages, excepting for the Land-use and Social and Environmental impacts indicators which mainly report outputs from the simulations without feed-backing to rest of the structure.
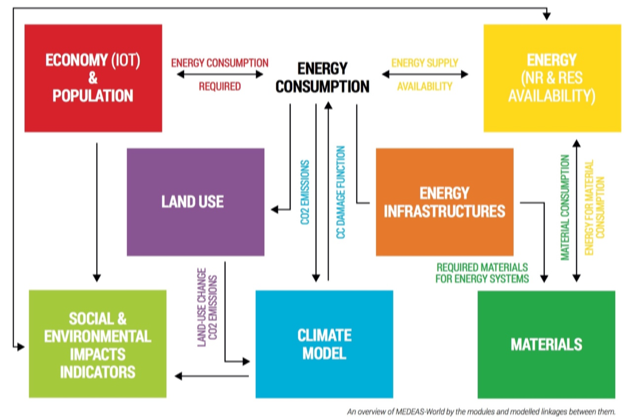
Overview of MEDEAS-World by modules and the modelled linkages between them


